GPP Pusat Data – KPKT – Translated and cleaned – 2 Definitions and Categories.
TL:DR: – Data Center definitions and categories as seen by the Malaysian planning staff. It is a simplification but when seen as a guideline then it is useful. Three categories is defined: Small Data Centers (1-5 MVA – 11kV) , Simple Data Center (5-25 MVA – 33kV), Big Data Centers (>25 MVA – 132kV, 275kV) .


- DATA CENTER DEFINITION AND CATEGORIES
2.1 DEFINITION
2.2 DATA CENTER CATEGORIES
2.3 TYPES OF DATA CENTERS
2.4 GENERAL
2.5 CHARACTERISTICS OF DATA CENTERS
2.6 DATA CENTER INDUSTRY PLAYERS DATA CENTER CLASSIFICATION
COMPONENTS IN A DATA CENTER BUILDING
2 DATA CENTER DEFINITION AND CATEGORIES
2.1 Definition
A Data Centers is a facility building used to centrally house ICT equipment and infrastructure for the purpose of managing data such as storing, collecting, processing and distributing data for an organization or company.
2.2 Data Center Categories
In terms of the power capacity of a Data Center, there are three (3) categories of Data Center development that have been identified:
Table 2.1 : DATA CENTERS Category
| Scale | Small Data Centers | Simple Data Center | Big Data Centers |
| Power capacity | 1-5 mega volts Amp (MVA) | >5-25 mega volt amp (MVA) | > 25 Mega Volt Amp (MVA) |
| Level Voltage | 11 kV | 33kV | 132kV, 275kV |
| Small Data Centers | Simple Data Center | Big Data Centers |
| Power Capacity: 1-5 MVA | Power Capacity: >5-25 (MVA) | Power Capacity: >25 (MVA) |
| Level Voltage: 11kV | Level Voltage: 33kV | Level Voltage: 132kV, 275kV |
| TNB Data Center | Infinaxis Data Center, Cyberjaya | BDC Data Center, Sedenak |
| Area: 2.62 Acres | Area: 3.08 acres | Area: 38.7 acres |
| Power Capacity: 4MVA | Power Capacity: 12MVA | Power Capacity: 145MVA |
| Expected Completion: 2024 | Expected Completion: 2025 | Operated: 2022 |
| Planning Zone: Commercial | Planning Zone: Commercial | Planning Zone: Industrial |

2.3 Types of Data Centers
In terms of operation and development of Data Centers, there are three (3) types of Data Centers, namely:
- Private Data Center (Enterprise)
Data Centers that are located on site which are built and placed within the premises of the organisation/company (on premises) or in other places (off premises) for private use and are fully managed by the organisation/company.
- Colocation
A colocation Data Center is a physical facility that offers space, racks, and infrastructure facilities for Data Center development such as power supply, cooling systems, network systems, and security aspects to host servers, storage, network equipment, and other IT infrastructure for an organization or company. These physical facilities are rented by colocation Data Center providers to customers in the form of cabinets, cages, or private suites.
Example: Equinix, Bridge Data Center, AIMS
- Hyperscale
A hyperscale Data Center is a data storage facility that can accommodate large amounts of data. These Data Centers are in demand from companies that require data processing with extensive storage requirements and are specially designed for their needs.
Examples: Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook and Apple.
2.4 General Characteristics of Data Centers
The general characteristics of a Data Center have 5 components which are:
- Safety
Data Centers need to be designed with security aspects in mind. These facilities need to be protected from physical and cyber threats, including theft, fire, and cyberattacks. To ensure the security of Data Centers, access is usually limited to authorized personnel only and security measures such as biometric authentication and surveillance cameras need to be in place.
- Infrastructure
Data Centers infrastructure consists of various components including servers, storage systems, networking systems, power systems and cooling systems. Data Centers require high-power systems to operate and they need to be cooled to prevent Data Center components from being disrupted. In addition, Data Centers also require backup generators, Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) and Dedicated Cooling Systems in their operations.
- Service
Data Centers provide a wide range of services including data storage, management, backup and recovery. It is also to support productivity applications such as email, high-capacity e-commerce transactions and online gaming communities. In addition, Data Centers are increasingly being used to support the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR4.0) such as Big Data, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence applications (Artificial Intelligent) and others.
- Cloud Storage and Exchange
Cloud storage and exchange is an online storage medium that allows users to store data/information in DATA CENTERS and then connect to a virtual server through cloud storage and exchange. This system will make it easier for customers to store and manage data, thereby ensuring data security.
- Management
The management of DATA CENTERS requires specialized expertise, knowledge of the latest technology, responsible for ensuring the efficient and safe operation of DATA CENTERS as well as the implementation of best practices in operating operations for the entire development of DATA CENTERS. In the context of the development of DATA CENTERS, there are three (3) existing mechanisms in the provision of DATA CENTERS, namely:
- Operation Company (OpCo)
OpCo is a company that manages DATA CENTERS that are rented/leased at the premises of the building owner. It also plays a role in securing tenants from potential companies.- Property Company (PropCo)
PropCo is the company that develops DATA CENTERS that provides rental space to OpCo. The company is not involved in the day-to-day program of the operation of DATA CENTERS.
- Operation Company (OpCo) & Property Company (PropCo)
The company that develops DATA CENTERS and at the same time also acts as a provider of data storage facilities.
- Property Company (PropCo)
2.5 Industry Players DATA CENTERS
Industry players for the development of DATA CENTERS are divided into three (3) namely:
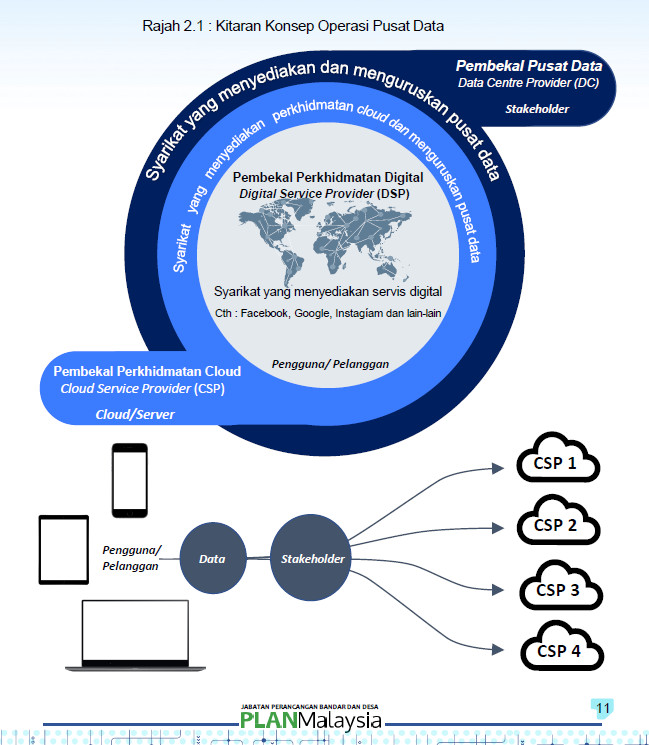
Figure 2.1 : DATA CENTERS Operating Concept Cycle
- DATA CENTERS Providers
- Data Centers Provider (DC)
- Stakeholder
- Digital Service Providers
- Digital Service Provider (DSP)
- Companies that provide digital services
- Ex: Facebook, Google, Instagíam and others
- Cloud Service Providers
- Cloud Service Provider (CSP)
- Cloud/Server
2.6 Classification of DATA CENTERS
Based on the Telecommunication Industry Association Standards for Data Centers (TIA-942) there are four (4) classifications of DATA CENTERS known as tiers. The following is a detailed table for each tier of DATA CENTER :-
Table 2.2 : Classification of DATA CENTERS
| Tier I Basic Site Infrastructure | Have single-capacity components for all DATA CENTERS hardware equipment.Have a single path or non-redundant component (N) for electricity supply and cooling system.Downtime rate of 28.8 hours per year.Uptime up to 99.671%. |
| Tier II Redundant Component Site Infrastructure | Has a single path for electrical supply, systemcooling and redundant components (N+1).It has an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), an additional generator set and is equipped with a raised floor.Downtime rate of 22 hours per year.Uptime up to 99.741% |
| Tier III Concurrently Maintainable Site Infrastructure | DATA CENTERS that have been recognized by International Standards.It has a fully redundant component (N+1).It has more than one (multiple) power supply, cooling system, UPS, auxiliary generator and is equipped with raised floors.Downtime rate of 1.6 hours per year.Uptime up to 99.982%. |
| Tier IV Fault Tolerant Site Infrastructure | Have hardware and component requirementsalmost the same development as Tier III.It has fault-tolerant redundancy (2N or 2N +1) and the highest level of safety.The downtime rate is 0.4 hours or 24 minutes per year.Up to 99.995% uptime |
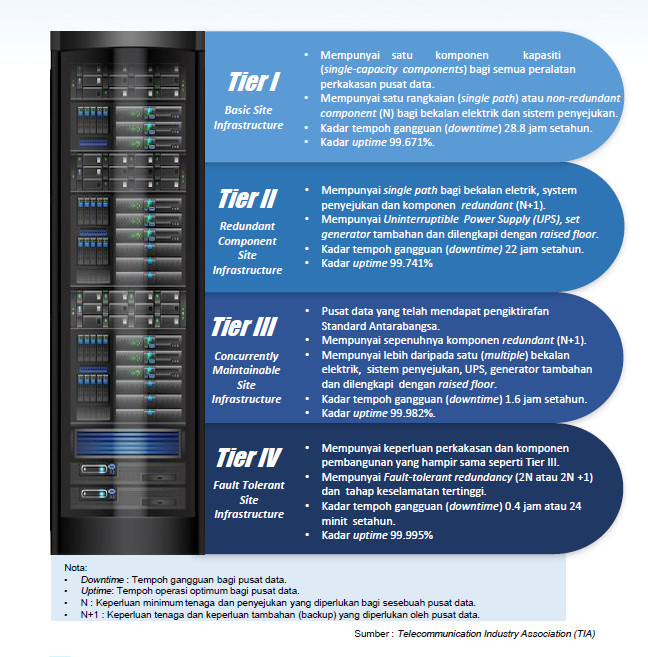
Notes:
- Downtime : Duration of outage for DATA CENTERS.
- Uptime: Optimal uptime for DATA CENTERS.
- N : Minimum energy and cooling requirements required for a DATA CENTERS.
- N+1 : Energy requirements and additional backup requirements required by DATA CENTERS.
Source : Telecommunication Industry Association (TIA)
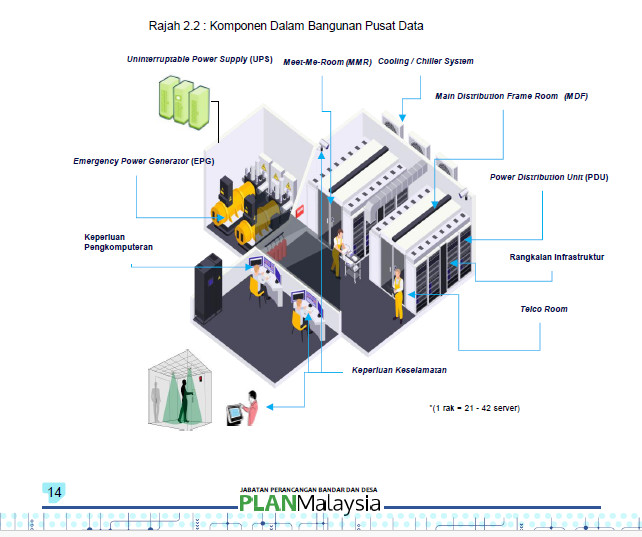
2.7 Components in the DATA CENTERS Building
There are eight (8) main types of development components in the DATA CENTERS building, namely:
- Computing Requirements
Covers desktops, servers and racks as well as other related hardware.
- Infrastructure Network
Including routers, switchers, modems, cables, and other components that connect DATA CENTERS with storage servers to users.
- Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS)
A UPS is a piece of hardware that serves as a prefix backup that will supply power to all electronic equipment in the event of a power outage.
- Cooling / Chiller System
This system works to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels inside the DATA CENTERS. This system consists of air conditioning, cooling and Computer Room Air Conditioning System (CRAH).
- Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
PDUs are equipment to control the flow of electricity supplied into the DATA CENTERS.
- Emergency Power Generator (EPG)
EPG is an equipment that contains generator sets and diesel for the purpose of backing up the electricity supply for DATA CENTERS.
- Safety Requirements
The security requirements required in the DATA CENTERS are such as CCTV, biometric devices, mantraps, firewalls, detection devices and fire extinguishers. Security guards must be provided along with a post guard and control room.
- Meet-Me-Room (MMR)
Meet Me Room is a space that brings together all cables and fiber for the purpose of data exchange.
- Main Distribution Frame Room (MDF)
The MDF Room is the space that connects the equipment inside the network facility to the cables and equipment inside the DATA CENTERS. Each cable supplying service to the consumer and Distributed via MDF to MMR to process data.
- Telco Room
Telco Room is a space to place all service providers operating in a DATA CENTER
Figure 2.2 : Components in the DATA CENTERS Building
- Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS)
- Meet-Me-Room (MMR) Cooling / Chiller System
- Main Distribution Frame Room (MDF)
- Emergency Power Generator (EPG)
- Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
- Needs
- Computing
- Infrastructure Network
- Telco Room
- Safety Requirements
- *(1 rack = 21 – 42 server)
 Previous Post
Previous Post